1. The basics of notifications
Notification in Checkmk involves actively notifying users when the state of a host or service changes.
Let us assume that at a certain point in time on the host mywebsrv17 the service HTTP foo.bar changes from OK to CRIT.
Checkmk detects this and by default sends an email including the most important data regarding this event to all contacts for this service.
The state later changes again, from CRIT to OK, and the contacts receive another email — this time reporting a recovery.
But this is only the simplest way of notifying. There are numerous ways for you to refine it:
You can send by SMS, pager, Slack, and other Internet services.
You can limit notifications to specific time periods, for example, to take on-call rosters into account.
You can define escalations if the responsible contact does not take action quickly enough.
Users can independently 'subscribe to' or 'unsubscribe from' notifications if you want to allow this.
You can generally define rules who is to be notified about what, and when.
However, before you start working with notifications, you should note the following:
Notification is an optional feature. Some users do without the notifications because they have a control center that is manned around the clock and that only operates with the status interface.
Initially activate the notifications only for yourself and make yourself responsible for everything. Observe over at least a few days how large the number of notifications is.
Do not activate notifications for other users until you have reduced the false alarms (false positives) to a minimum. We have described how you can do this in the chapter on fine-tuning monitoring.
2. Preparing for email notifications
The simplest and by far the most common method is to send a notification by email. There is enough space in an email to also include the graphs of metrics as well.
Before you can notify by email, your Checkmk server must be set up for sending emails. For all supported Linux distributions, this boils down to the following:
Install an SMTP server service. This is usually done automatically during the installation of the distribution.
Specify a smarthost. You will usually be asked for this when installing the SMTP server. The smarthost is a mail server in your company that takes over the delivery of emails for Checkmk. Very small companies usually do not have their own smarthost. In this case, you use the SMTP server supplied by your email provider.
If the mail dispatch has been set up correctly, you should be able to send an email from the command line, for instance via this command:
The email should be delivered without delay.
If this does not work, you will find clues as to the source of the problem in the SMTP server’s log file in the /var/log/ directory.
More details on setting up mail delivery under Linux can be found in the article on notification rules.
3. Activating email notifications
Once the email dispatch is basically working, activating the notification is very simple. In order for a user to receive notifications by email, the following conditions must be fulfilled:
An email address has been assigned to the user.
The user is responsible for hosts or services — through the assignment of contact groups.
There is a notification rule that ensures that the members of the contact groups are notified by email.
Assigning email address and contact groups is achieved via the user’s properties, as we showed earlier in the chapter on user administration. It can be done for instance by adding your email address and the Everything contact group to the user account named cmkadmin. Checkmk already has pre-configured notification rule that notifies every contact for the hosts and services about important status changes using HTML mail.
You can find out what ‘important’ means in the next section.
4. Testing notifications
It would be a bit cumbersome to wait for a real problem or even provoke one to test the notifications. This is easier with Test notifications, a tool with which you can simulate a notification for a host or service and have the notification sent immediately.
First open the notification center with Setup > Events > Notifications:
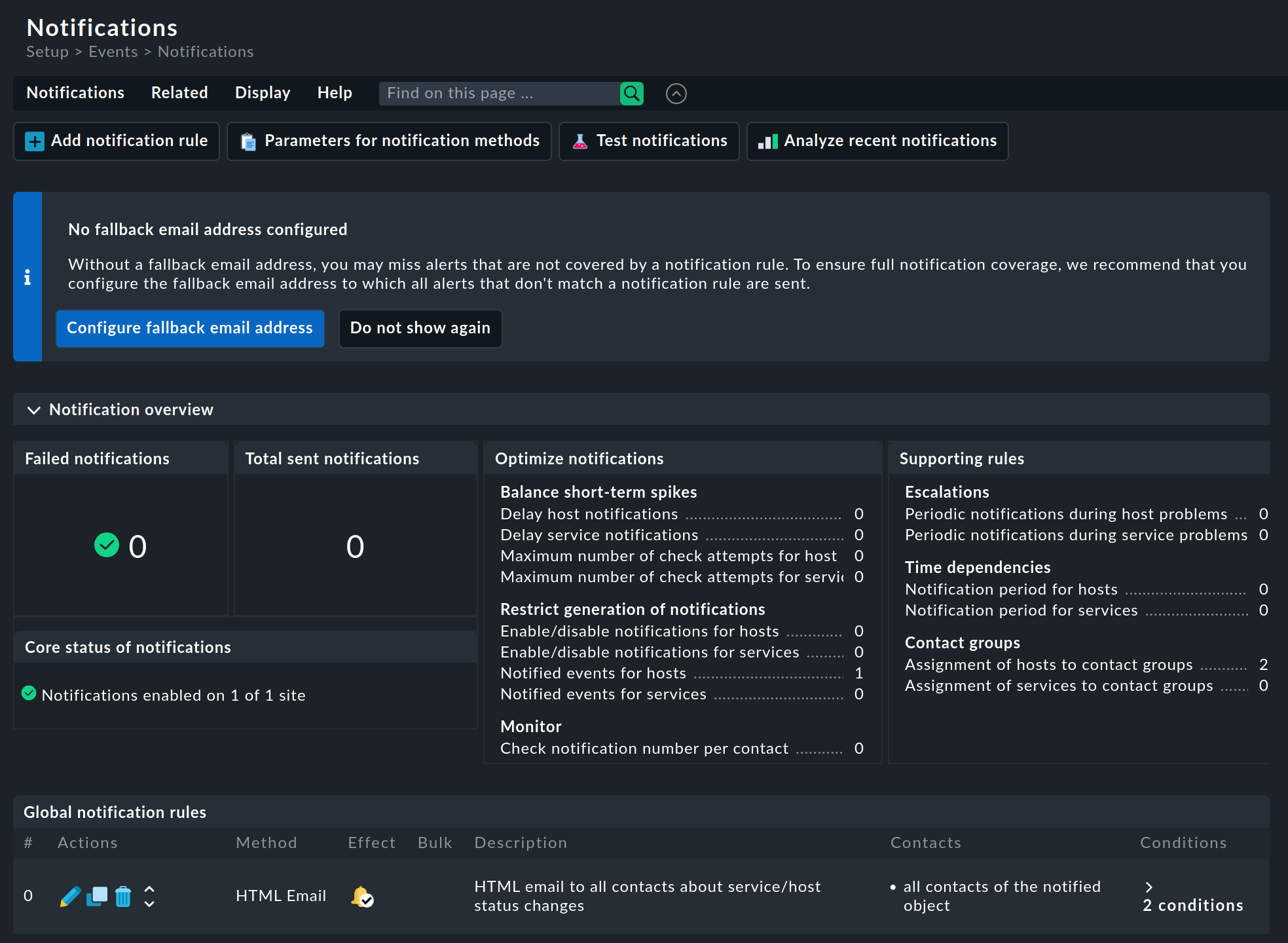
When you call up this page for the first time, you will be informed about the 'fallback email address' that has not yet been configured, as can be seen in the above screenshot. This information can be ignored for the moment. We discuss this topic in the article on notification rules. Until you have read this section, we recommend leaving the information as a reminder and not clicking on Do not show again to remove it.
Otherwise, this page shows status information — such as the number of sent and failed notifications — and it is used to call up actions relating to the topic of notifications, e.g. the creation of a notification rule, but also the calling up of host and service rules that can influence notifications.
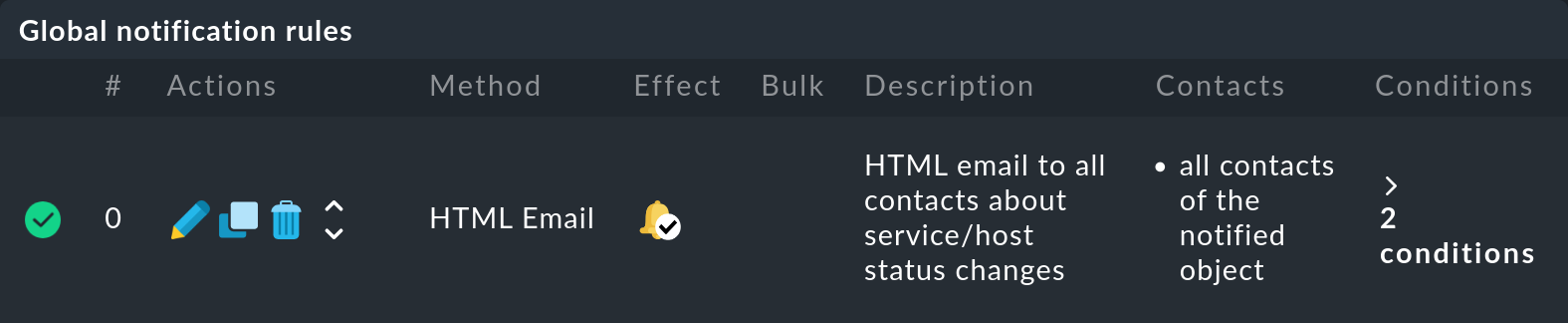
At the bottom of the Notifications page, in the Global notification rules box, the global notification rule supplied by Checkmk is displayed. 'Global', because every user can also create their own, user-defined notification rules.
The supplied notification rule ensures that notifications of all important status changes of hosts and services are sent to all responsible contacts via HTML email. All status changes of hosts to DOWN and UP, and of services to CRIT, WARN and OK are classified as 'important'.
The notification test evaluates the notification rules displayed. You can access the notification test via Setup > Events > Notifications and the Test notifications button:
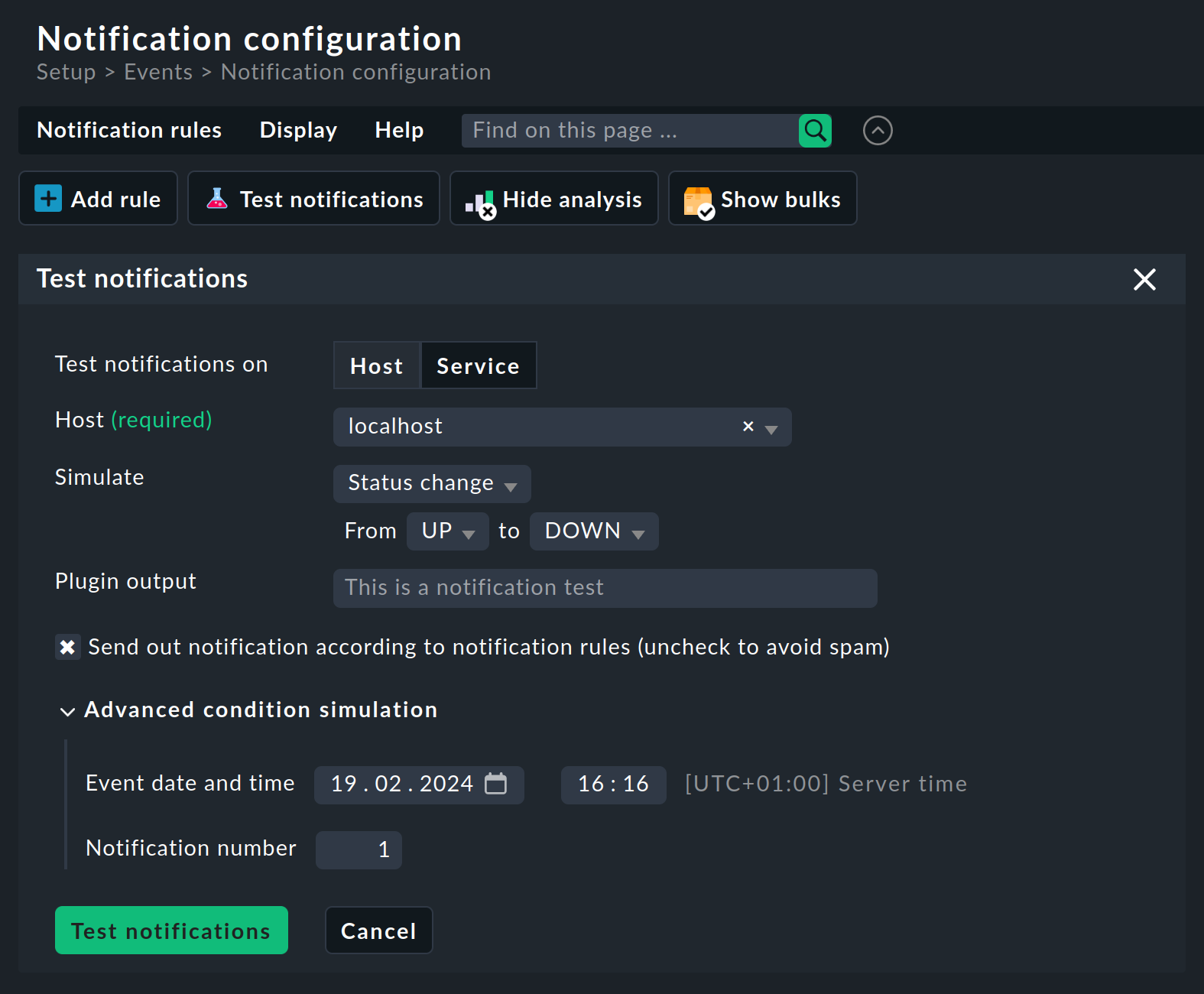
Simply select a host and then any state change as the event. By activating the Trigger notification for a specific method checkbox, you specify that the notification is not only simulated but also actually sent.
Click on Test notifications. The results are displayed at the bottom of the page. The most important is the summary Test results at the top:
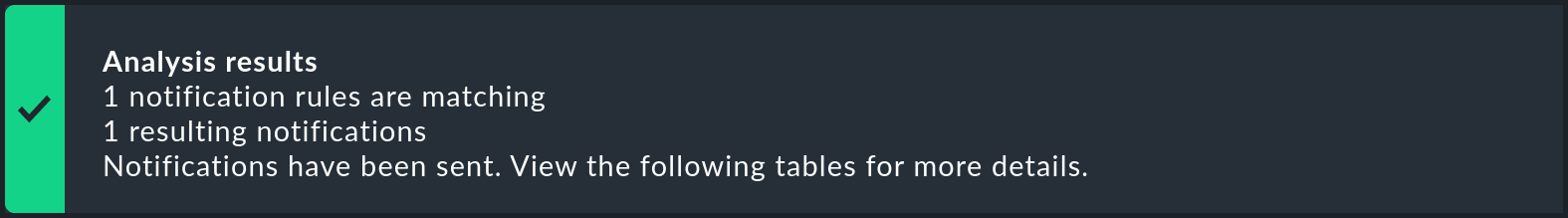
For the test to be successful, at least one notification rule must match. The message containing notification has been triggered indicates that the notification has actually been sent.
Under Predicted notifications you can then see to whom and via which channel the notification was sent:
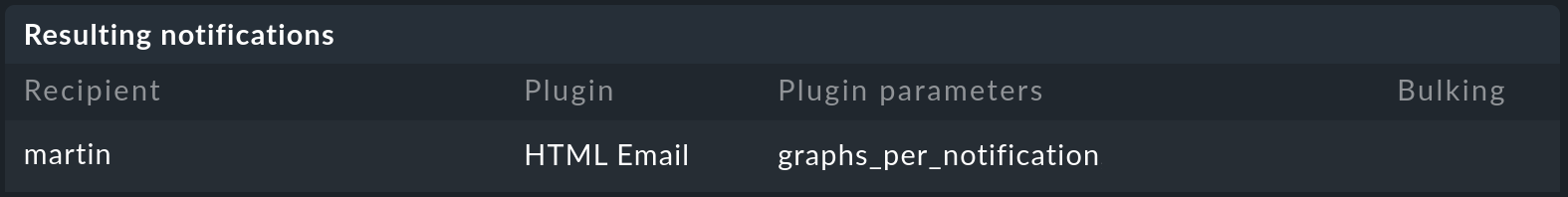
Finally, the first column in the bottom field shows which of the notification rules has taken effect ![]() , and which has not
, and which has not ![]() :
:
This should immediately result in an email for this simulated problem. A detailed description of the options and the results for the notification test can be found in the article on notification rules.
If you have not received a notification in real monitoring, i.e. outside of the simulation, this does not necessarily mean an error. There are situations in which the notifications from Checkmk are deliberately suppressed for example:
when the notification has been disabled Master control snap-in;
when a host or service is in a scheduled downtime;
when a host is DOWN and therefore no notifications are triggered by its services;
if the status has changed too often recently and the service has therefore been marked as
 flapping.
flapping.
5. Fine-tuning notifications
You can adapt the notifications in Checkmk to your, or your organization’s, needs in a variety of ways by means of complex rules. You can learn all of the details for this in the article on notifications.
6. Troubleshooting
The notification module in Checkmk is very complex — because it covers many, very different requirements that have proven to be important over many years of practical experience. The question "Why didn’t Checkmk notify here?" will therefore be asked more often than you might expect, especially at the beginning. For this reason, here are a few tips for troubleshooting.
For problems with notifications, first check whether there are any failed notifications. These are listed on the Monitor > System > Failed notifications page. The Summary column shows the reason for the error — or at least gives you an indication of the probable cause.
Another possibility is offered by Checkmk by analyzing the most recent notifications that the system has generated and which have passed through the notification rules. Open the table of notifications for analysis with Setup > Events > Analyze recent notifications. Here you can resend a notification, display its context and analyze its associated notification rules. You can find more information on this in the article on notifications.
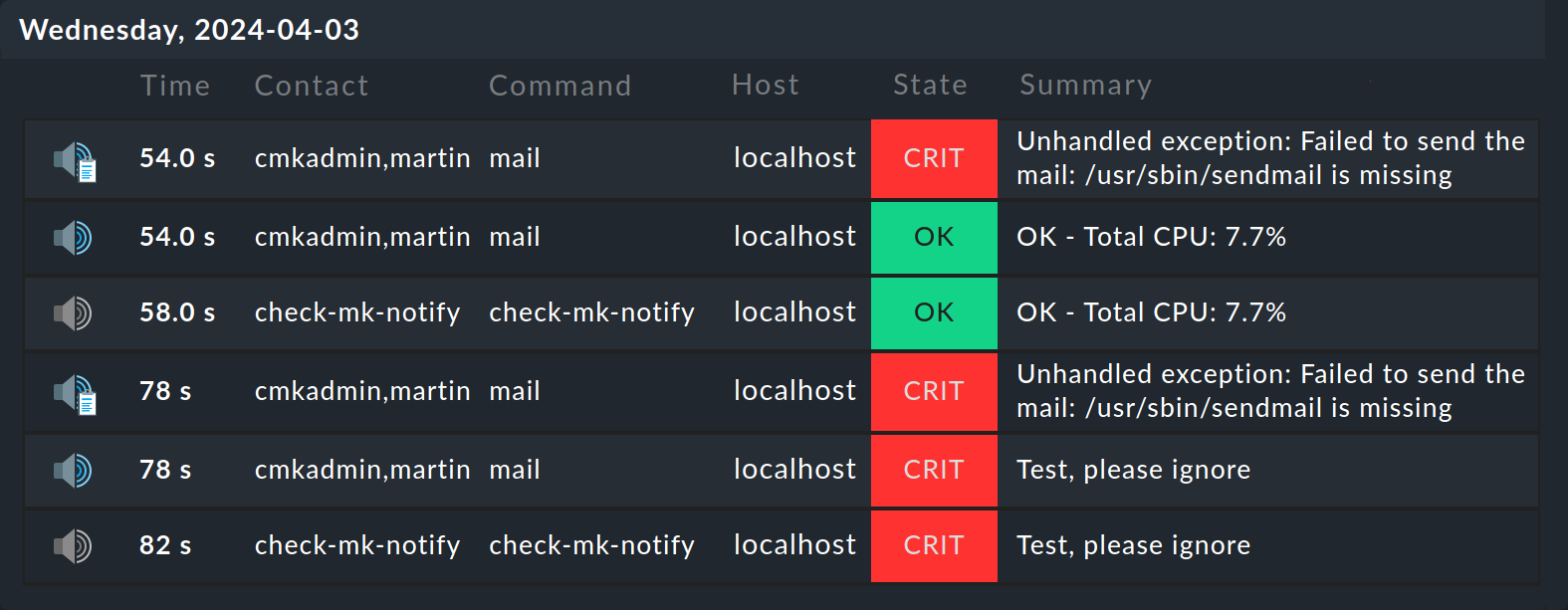
If a notification has not been triggered by a particular service, the first step would be to check the history of the notifications for that service. To do this, open the detail page for that service by clicking in the monitoring on the service. Select Service > Service notifications from the menu. There you will find all notification events for this service listed chronologically from the most recent to the oldest.
Here is an example of a service for which notification was attempted, but for which the sending of emails failed because no SMTP server has been installed.
You can find even more information in the file ~/var/log/notifiy.log.
You can view this as a site user, with the less command, for example:
If you are not yet familiar with less — with the key combination Shift+G you can jump to the end of a file (which is useful for log files), and quit less with the Q key.
With the tail -f command, you can also observe the file contents 'live' while it is running.
This is useful if you are only interested in new messages, i.e. those that only appear after tail has been entered.
Here is an excerpt from the notify.log for a successfully triggered notification:
2024-04-15 16:21:47,912 [20] [cmk.base.notify] Analysing notification (localhost) context with 14 variables
2024-04-15 16:21:47,912 [20] [cmk.base.notify] Global rule 'Notify all contacts of a host/service via HTML email'...
2024-04-15 16:21:47,913 [20] [cmk.base.notify] -> matches!
2024-04-15 16:21:47,913 [20] [cmk.base.notify] - adding notification of martin via mail
2024-04-15 16:21:47,913 [20] [cmk.base.notify] Executing 1 notifications:
2024-04-15 16:21:47,913 [20] [cmk.base.notify] * notifying martin via mail, parameters: graphs_per_notification, notifications_with_graphs, bulk: no
2024-04-15 16:21:47,913 [20] [cmk.utils.notify] sending command LOG;HOST NOTIFICATION: martin;localhost;DOWN;mail;
2024-04-15 16:21:47,913 [20] [cmk.base.notify] executing /omd/sites/mysite/share/check_mk/notifications/mail
2024-04-15 16:21:48,458 [20] [cmk.base.notify] Output: Spooled mail to local mail transmission agent
2024-04-15 16:21:48,501 [20] [cmk.utils.notify] sending command LOG;HOST NOTIFICATION RESULT: martin;localhost;OK;mail;Spooled mail to local mail transmission agent;Spooled mail to local mail transmission agentIf you want to know exactly when notifications are generated — and when they are not — you can learn the whole truth in the article on notifications. |
By setting up the notifications, you have completed the finishing touches — Your Checkmk system is ready for use! This does not mean, of course, that the full capabilities of Checkmk have been fully explored.
